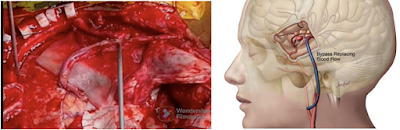
BRAIN BYPASS (Extracranial –Intracranial) - FOR WORLD’S LARGEST CAVERNOUS ICA( INTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY )ANEURYSM.
She was evaluated outside with CT brain which was reported as skull base lesion ?meningioma.
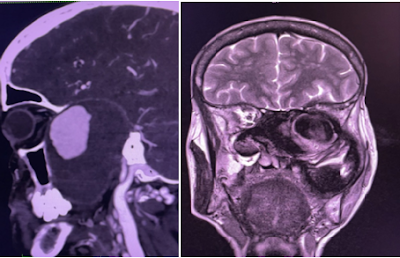
CT ANGIO - Showed a very large aneurysm noted arising from the horizontal segment of cavernous segment of left internal carotid artery measures about 10.5 cm in cranio-caudal extent x 7.5cm in antero- posterior extent x 5.9cm in transverse dimension. The patent lumen of the aneurysm shows avidly enhancing area measures about 4.3 x 2.9 x 2.8cm.
CT ANGIOGRAM
Aneurysm was very large and was eroding and destructing posterior wall of orbit , sphenoid bone , clinoid , Maxilla , petrous bone , clivus , mandible and molar tooth . It was extending from anterior cranial fossa base to molar tooth down .
With ill-defined large hyperdense areas surrounding the avidly enhancing lumen - suggestive of thrombus.
Treatment STRATEGY.
- 1) DSA ,baloon occlusion test and plan for flow diverter/ trapping .
- In view of financial issues - they deferred the above option.
- 2) Surgery -
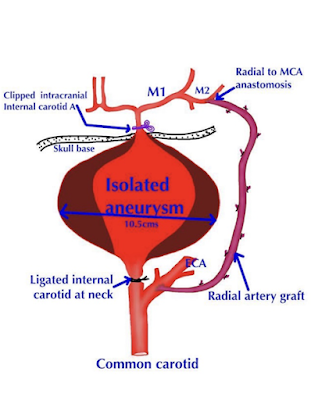
- A) Extra-cranial - intracranial Bypass using Radial artery graft.
- B)Trapping of aneurysmal segment of ICA
OVERVIEW
Cerebral bypass surgery is a procedure to restore blood flow to the brain by redirecting blood around blocked, narrowed, or damaged ( aneurysms ) arteries. The operation uses a blood vessel from another part of the body or reroutes a donor artery from the scalp onto the brain. The arteries are surgically joined with sutures to supplement or replace blood flow in that area.
A cerebral bypass is the brain's equivalent of a coronary bypass in the heart.
The goal of bypass surgery is to restore blood supply to the brain and prevent strokes or death due to underlying vascular disease .
This can be performed to supplement blood flow when small arteries are narrowed (“low-flow” bypass) or replace blood flow when medium-to-large blood vessels need to be sacrificed during complex brain surgeries (“high-flow” bypass).
Who is a candidate?
• An aneurysm, tumor, or atherosclerotic plaque that is not treatable by endovascular or other means
• Failure of medication to control TIA symptoms or stroke or Moya moya disease
Pre-op key investigation
- Imaging tests (angiogram, CTA, MRA) that show arterial stenosis or occlusion.
- Cerebral blood flow studies (CT perfusion, PET, SPECT) that show arterial stenosis is causing insufficient blood flow to the brain.
- DSA & Balloon test occlusion is used to evaluate whether one artery can be temporarily or permanently blocked without significantly affecting the level of blood to brain.
What are the risks?
- Stroke can occur from manipulation and temporary clipping of the arteries in the brain. It can also occur from graft failure, or failure of blood to flow adequately though the newly connected arteries.
- Seizures are a risk with any brain procedure.
- Swelling and/or bleeding in the brain can occur in response to an increase in blood flow to brain areas that were formerly receiving very low amounts. Symptoms of hyper-perfusion injury include headache, facial/eye pain, or other neurological deficits.
- Graft occlusion occurs when blood clots form inside the donor vessel blocking off the blood flow.
STEPS of EC-IC BYPASS .
After general anesthesia. Patients head is placed in a 3-pin, Mayfield skull-fixation device, which attaches to the table. Painting and draping of scalp , left side neck and upper limb is done.
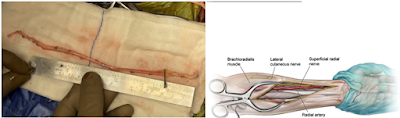
1. Harvesting Radial artery graft ( RAG) from left hand ( after normal arterial Doppler study ) . Branches arising form vessel are clipped preparing it for anastomosis . Graft filled with heparinised saline to prevent thrombosis .
3) Question mark skin incision made to expose left fronto-temporal region . Superficial temporal artery exposed and temporalis muscle raised.
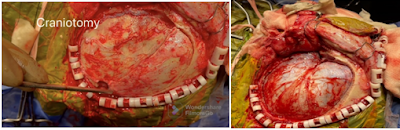
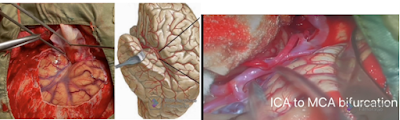
4) Craniotomy and Clinoidal drilling done to expose the proximal ICA ( ophthalmic segment ) for trapping aneurysm . After burrhole , craniotomy is done . The bone flap is lifted and removed to expose the thedura. The dura is opened and folded back to expose the brain.
5) Dissection of arachnoid to expose ICA and M2 inferior trunk for anastomosis . Working under an operating high end microscope, the surgeon carefully locates a branch of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) suitable for bypass. The size of the recipient vessel must be a good match for the diameter of the donor vessel.
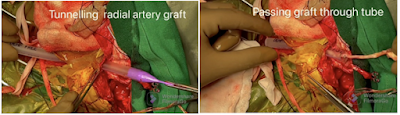
6) Tunnelling of radial artery graft(RAG) from neck to brain using chest tube - check to avoid kinking.
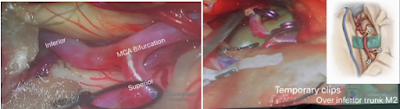
7) Anastomosis of inferior trunk of M2 to RAG (Radial artery graft )and confirming the patency. Temporary clips are placed across the donor and recipient vessels to stop the blood flow. The graft vessel is cut and the end prepared for anastomosis. The surgeon then makes an opening in the side of the MCA vessel and sutures the two blood vessels together.
8) Anastomosis of ECA with RAG after temporary clip over graft proximally.
9) Ligation of ICA in the neck.
10) Permanent Clipping of ophthalmic segment ICA.
11) Confirmation of graft patency using Doppler . After the vessels are anastomosed , the surgeon releases the temporary clips and verifies there are no leaks.
12) Aspiration of blood from trapped segment of ICA - this collapses the size of fundus of aneurysm.
13) Closure of wounds .
The dura is closed with sutures. The bone flap is replaced, but a hole is enlarged to allow passage of the bypass vessel without kinking or pressure. The bone flap is secured to the skull . The muscles and skin are sutured back together. A dressing is placed over the incision. Similarly neck and left upper limb wounds are closed after achieving haemostasis .
OUR TEAM
OUR TEAM FOR BYPASS.
Dr. Shivashankar B. Marajakke
Chief neurosurgeon
Dr .Prakash Bharamagoudar
Chief Neuroanaesthesist& Medical superintendent
Dr. Amol Bhoje & Dr. Shrikant Kole.
CVTS surgeon
Dr .Vishwas Bhosle, Dr.Nishad Sathe, Dr.Swapnil Valiwade, Amar, Sagar, Prakash.
Assistance
..........................
POSTOPERATIVE PERIOD.
Patient extubated on table , neurologically no fresh deficits .
Postop CT Angiogram study
Complete non filling of aneurysmal segment of ICA and satisfactory graft patency with very good flow .
Patient discharged in good condition on postop Day 10 after suture removal. She is neurologically and vitally stable .Right eye vision is gradually improving
CONCLUSION.
With Proper understanding of disease , strategic planning , finest technological ( infrastructure) support , skilled Neurosurgeon/ Neuroanaesthetist and OT /ICU team , any kind of complex challenging procedures and best of results can be achieved even at village level charitable hospital like Siddhgiri Hospital and Research Centre Kanerimath.
With such a state of art Neuro set up , we are one among very few centres of India for rare, complex and challenging epilepsy surgeries , endoscopic brain surgeries and such complex neuro vascular surgeries- offering them beyond financial barriers
...................
Other Links
Social Links
www.youtube.com/Siddhagiri hospital